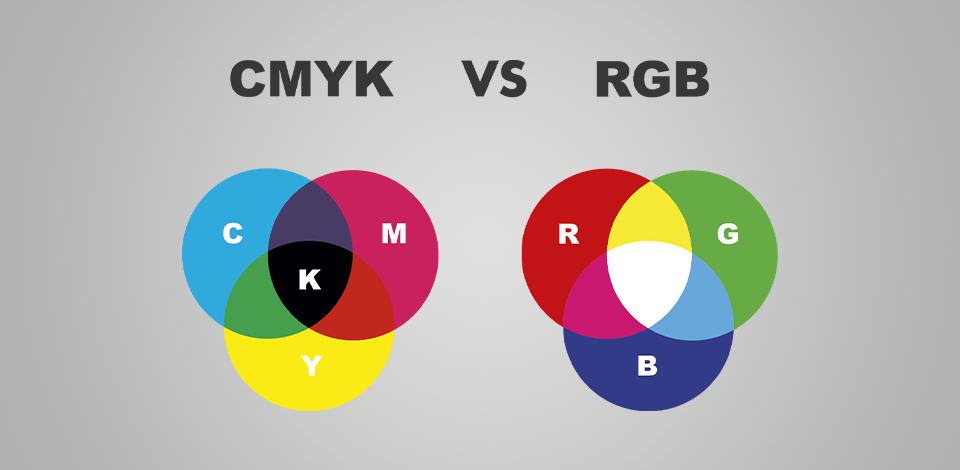
Every designer, photographer, and retoucher should know the difference between RGB and CMYK color modes, so if you are starting in Photoshop color modes, this article may come in handy. The way your photos and design projects look after post production depends on which color profile you choose. While RGB is a go-to variant for digital imagery, CMYK works best for printed media.
When creating designs, you should be very careful with the color profile you choose and make a conversion if needed. It happens sometimes that a person uses an RGB color mode for printing materials and feels really confused when the colors look different from what is displayed on a computer monitor.
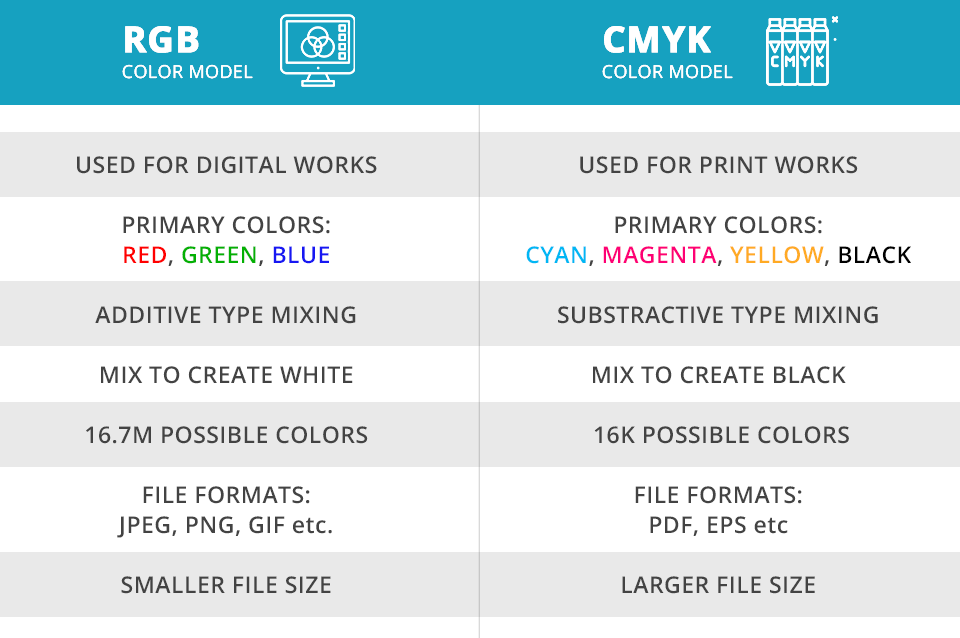
The most important difference between RGB and CMYK profiles is their intended use. While RGB is great for digital designs (images for posts, social network ads, etc.), CMYK fits the bill if you are going to print your projects (T-shirts, banners, business cards, and the like).
Other factors to keep in mind are primary colors, mixing mode, and maximum color yield. RGB relies on additive color creation when light is involved in the process. This profile consists of 3 main colors combined for producing white light.
As for CMYK, you can perceive it as the opposite process. It involves subtractive techniques and there is a pigment responsible for creating and mixing colors. Cyan, magenta and yellow are combined for making black.
The color combos in RGB max at 16.7 million colors and this number reaches just 16,000 for CMYK. In most cases, if you are going to print your photo, you need to turn it into a CMYK color profile. Doing that is easy with most photo editing software for PC. Though RGB files offer more color options, they are usually smaller than CMYK files.
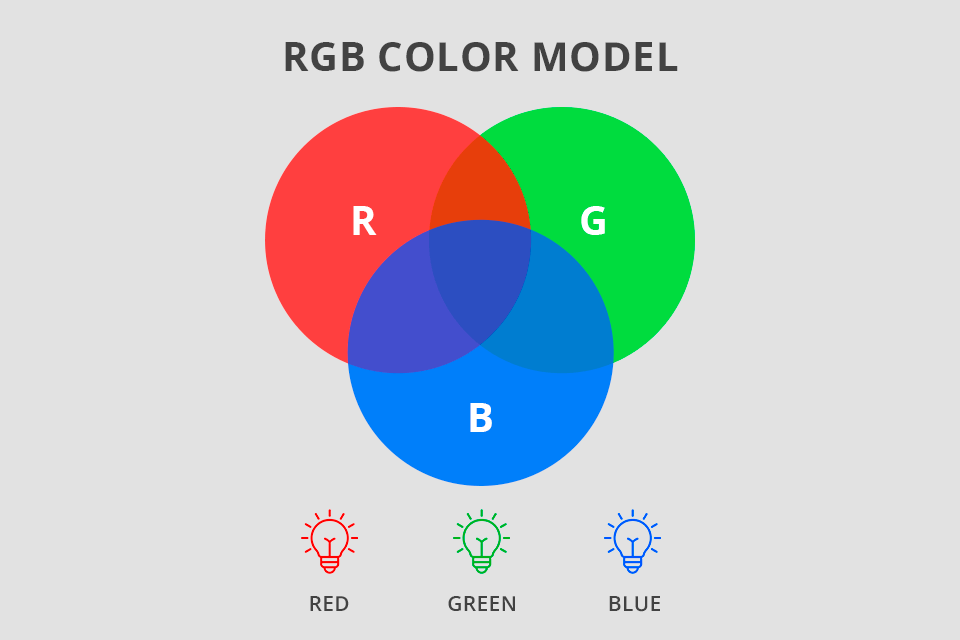
When you open photos, designs, texts, etc., on your computer, they will be displayed with varied combinations of red, green, and blue. That’s where RGB comes from. Screens employ hundreds of pixels to make and display images. All pixels are further divided into 3 sub-pixels – red light, green light, and blue light, which may have different intensities.
When you use RGB, you actually work with 3 key colors, namely, red, green, and blue. However, since their intensity may be different, you will see variations in resulting colors. For instance, when all 3 colors are combined and displayed at the highest degree, you will see white color. When the values are kept at the lowest point, there will appear black color.

The RGB additive color system is developed in accordance with human vision. We have 3 types of cone photoreceptors in our eyes, each of which is responsible for “discerning” red, green, and blue light waves. This information is further transmitted to our brain which interprets it and allows us to perceive a whole spectrum of tones and shades.
When you work with 3 main colors on a computer, you can fine-tune saturation, vibrancy, and shades by altering the source colors. Since this process is performed digitally, it actually boils down to adjusting the way light is manifested on the screen for making up a specific color.
You should use RGB and SRGB color profiles for designs that will be viewed on digital screens of laptops, tablets, phones, TVs, cinema screens, and even camera displays.
So, comparing CMYK vs RGB, you should opt for the second option if you create:
Web & app design: icons, buttons, graphics
Branding materials: online logos & ads
Social media: images for posts, profile pictures & backgrounds
Visual content: video, digital graphics, infographics, photographs for website, social media, or apps
JPEG is great for saving RGB files if you want to maintain the balance between file size and quality. This format is supported by almost every device.
PSD is the best format for RGBs if you need to share info with your colleagues and you all use Photoshop for work.
PNG format supports transparency, which is important for graphics that are supposed to be superimposed over others. You should choose this variant for UI elements – icons, banners, and buttons.
GIF is a wonderful option for saving animations – dynamic logos, bouncing icons, etc.
When working with RGB files, you’d better avoid such formats as TIFF, EPS, PDF, and BMP. They take up much space and are compatible with a limited range of programs.
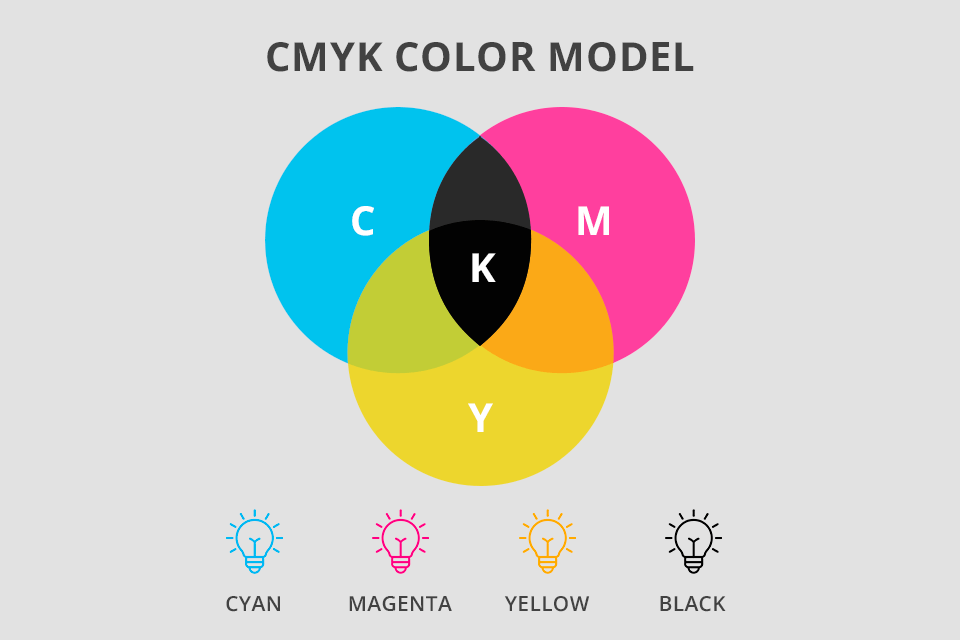
Which color model is used in printed designs? CMYK color profile and that is for a reason. It is based on 4 main colors, namely, cyan, magenta, yellow, and black. They are mixed in different variations for producing various colors.
A CMYK color scheme is of a subtractive nature. When you start printing a CMYK design, a machine creates a photo by combining 4 major colors with physical ink. If these colors are mixed with 0% degree – the resulting color is white. When you set the value to 100%, you will receive black color.

The main problem with CMYK prints is that they turn out dimmer and less vivid than what you see on the screen. To get specific tones in a printed design, you may need to initiate several test prints and customize settings in the process.
Currently, the RGB vs CMYK print debate is less discussed because most home printers are capable of printing images using the full RGB spectrum. Powerful professional machines used for large-scale projects use a CMYK color profile.
You should prefer CMYK to RGB color mode if you are going to print out your images instead of viewing them on a screen. It is an ideal variant in case your designs require mixing of colors with ink/paint. A CMYK color profile guarantees more accurate results.
So, you should choose CMYK for:
Branding materials: business cards, stationary, stickers, signs & storefronts
Advertising: billboards, posters, flyers, vehicle wraps, and brochures
Merchandise: T-shirts, hats and other branded clothing, pens, mugs, etc.
Essential materials: product packaging and restaurant menus
PDF is suitable for saving CMYK content thanks to rich compatibility.
AI is a standard source file for CMYK. You should choose it for teamwork, especially if you use Adobe Illustrator for most tasks.
EPS is a wonderful alternative for AI as it is compatible with many software.
However, before choosing any format, you’d better read the characteristics of your printer to understand what extension it supports.
If you do this, you are likely to get colors that differ a lot from what you see on your screen. This is specifically disappointing if you need a specific finishing. Though some top-notch printers may perform RGB > CMYK conversion, you will still receive prints with washed-out colors. So, it is highly advisable to save your files in CMYK before printing them.
It happens because some colors can’t be accurately reproduced in prints. They are called “out of gamut” colors. These can be metallics and fluorescents. Since an RGB color space consists of a much broader range of colors, many of them are missing in CMYK.
RGB is undeniably the best option for all digital imagery, while CMYK is unrivaled when it comes to printing.
From the technical point of view – no. It is necessary to convert them to CMYK before printing or let your printer do that instead of you if it has such a function. Not so long ago, there has appeared a new technique for printing RGBs but it is expensive and not very popular.
Head to the Ps Image tab. There will appear a drop-down menu > go to Mode. Have a look at the checked profile – it can be either RGB or CMYK.