Even if you have little editing experience, you are likely to come across the term “rendering”. This notion can cause some confusion as it can be interpreted in different ways and things get even more perplexing considering that one and the same term has different meanings in photography and 3D graphics. With this in mind, I decided to cover the topic of image rendering in detail, as well as to characterize the rendering process and its importance.

Googling rendered image meaning, you will get lots of different answers. In general, rendering is the procedure of converting pre-programmed or recorded datasets into 2D or 3D images. In photography, this process can denote several actions but they all stem from the same root, which defines how a device or browser translates image data into a viewable format. So, a device “sees” a dataset, which is the visual properties of an image or graphic. The way it renders the info affects the result you’ll see on the screen.
If the description of a photo consists of numerous details, you’ll have to wait relatively long till the process will be over. Besides, this is a rather difficult task for any computer and it will have to work at its full tilt. As for video rendering, which involves analyzing a series of pictures, the load on your system and the overall time doubles. So, the more powerful the computer you have, the quicker the rendering procedure will be.
Rendering can be of 2 types – pre-rendering and that performed in real-time. In real-time rendering, all calculations and data gathering are performed as a response to user actions right after those were made. If you want to enjoy a smooth experience, you need to use graphics hardware accelerators.
As the name implies, pre-rendering involves similar calculations needed to produce a rendered image, but they are done before a picture is displayed. Those who create visual effects and animations typically deal with pre-rendering. The biggest advantage of this type is that the quality of graphics is higher because there is more time to analyze data.

Your first experience with handling rendered photos takes place right during shooting when a camera interprets the info captured by an image sensor and then turns this data into a picture.
So, an image that appears on an electronic viewfinder or/and LCD screen is the result of your device rendering a scene. The way this picture looks fully depends on how your camera “perceives” the object you are photographing and the settings you use. Every device is unique in this regard.
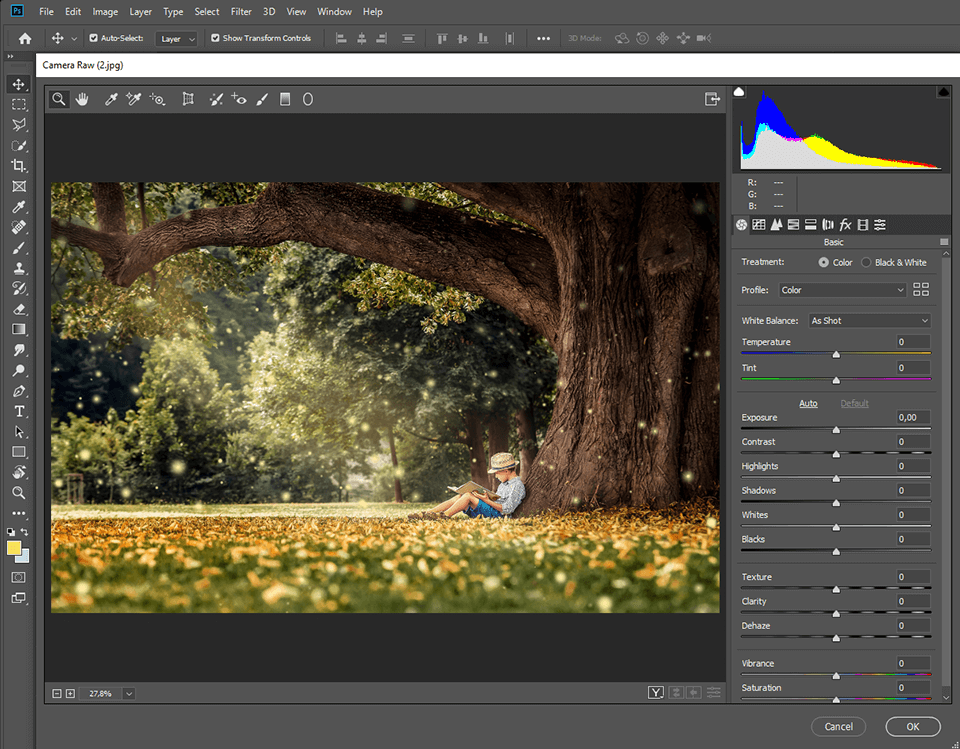
The next photo rendering is performed during the post-production phase. Every program employs unique algorithms to discern the data of a file and then renders it based on the screen you are using for work. Similar to cameras, each editing software for photographers copes with the task in its own way. If you want to get accurate results, you should use Photoshop, or Lightroom.
If you edit JPEG images, there will be no difference in the output. However, seasoned photographers recommend shooting in RAW, since this is the highest quality image format and stores virtually all data concerning files. Of course, RAW images take more place than JPEGs, but they contain more details needed for meticulous editing.
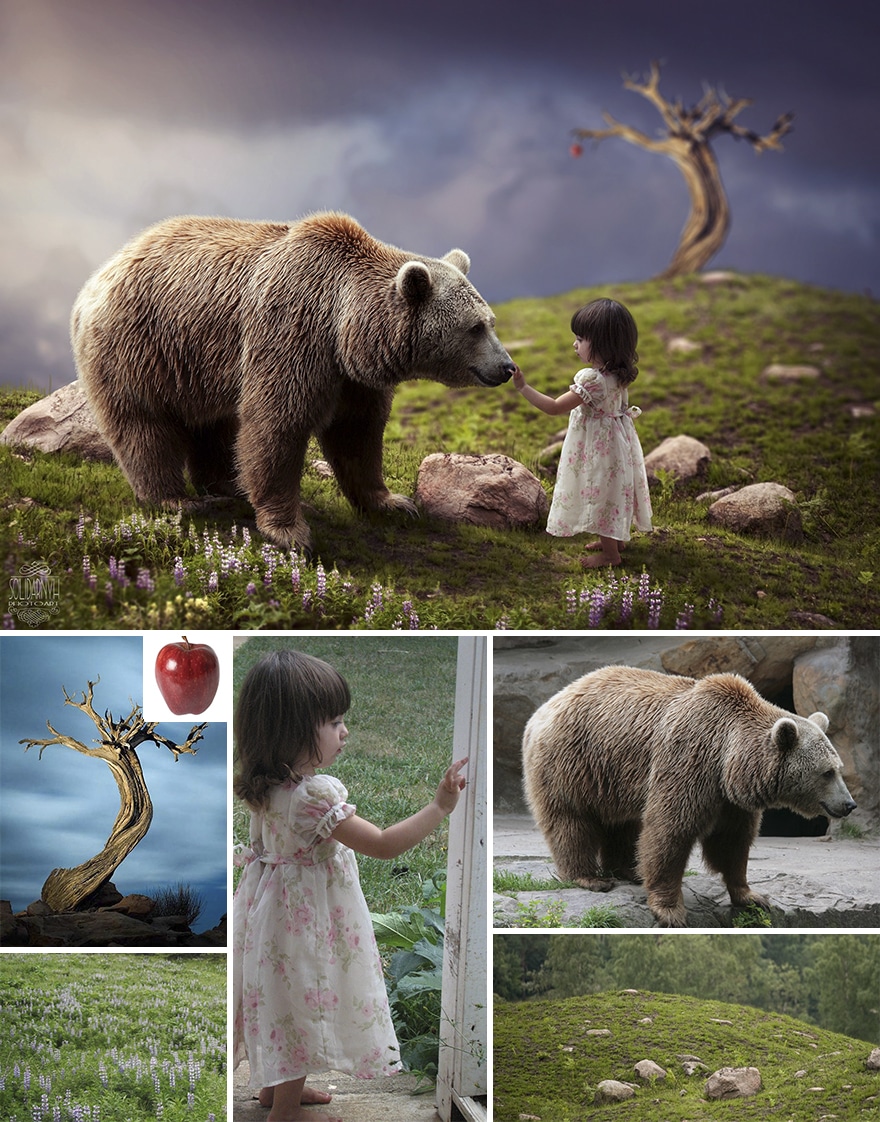

What is a rendered image if we are talking about creating a composite picture? In this case, we refer to datasets of a photo that consists of separate layers. You can use this approach if you want to bring to life levitation photography ideas and other Photoshop manipulation ideas.
We can also use the term for describing a final photo that consists of all the layers accurately combined. Some experts define this process as the “final render” but it is typically associated with 3D image rendering.

Video rendering involves managing image, audio, text, and graphics layers that are first processed individually. Next, you need to create a general composition in video editing software for Windows or Mac by aligning all tracks on a time axis. At the final stage of the process, all separate files are combined into a full-fledged playable video file. This is a reasonable space-saving move, allowing you to store and play numerous videos without cluttering disk space.
In visual effects-heavy projects, such as movies, TV shows, and animations, video rendering is used to combine live-action footage with computer-generated imagery (CGI) or other effects. This process creates the illusion of cohesive and realistic scenes. In live broadcasts, video games, and real-time presentations, video rendering happens in real-time to generate the graphics and visual effects that the audience sees on the screen.

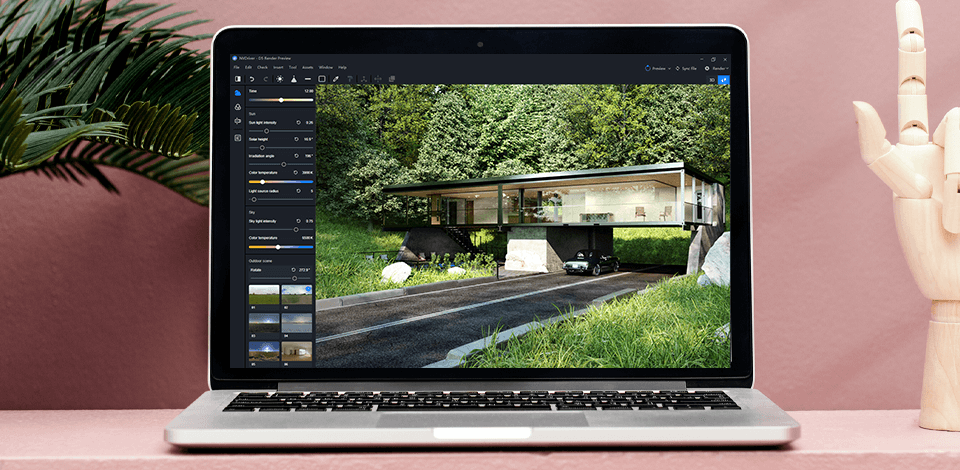
Digital models and objects are the main constituents of design, architecture, animation, and construction. They are needed to underpin a specific idea in a realistic and eye-pleasing manner. For such a task, experts use RAW data to describe objects and scenes composed in HTML, XML, and SVG. These descriptions include both geometric characteristics of items as well as info about their surface structure, colors, light sources, etc.
Once the info is collected, you need to use paid or free rendering software to generate a final object. Many users, especially seasoned ones opt for Adobe Aero download. At this stage, the program processes RAW data to put less load on PC memory and performance. If needed, you can also use Photoshop for architectural renderings.

Do you want to embellish your photos with offbeat effects and mesmerizing color mixes? Then you should download this collection of high-quality tools. There are over 2000 filters in the pack and they are suitable for different types of photos. Using them, you can significantly speed up your workflow. Just make sure you know how to install Lightroom presets on Mac & Windows and get down to work.